IASO’s key assets
The core distinction lies in how IASO integrates advanced geospatial data management into each module of the platform, allowing the following assets that are not always available in other similar tools.
1. Geo-structured data collection
IASO allows users to define on the web app detailed geographic hierarchies and units—such as country, province, district, facility—and link all data collection activities to this structure. When collecting data from the field, IASO mobile app users have to first select their geographical unit which has been predefined on the web interface, ensuring accurate data collection.
2. Decentralisation of responsibilities according to users’ geography
With IASO, web and mobile app users can be restricted to their assigned geographies (i.e. their region, their district, their village). This applies equally to data collection forms management, data validation, and user management, ensuring clarity, accountability, and local ownership.
IASO also provides built-in versioning for both forms and geographic data. Changes in a location’s name, boundaries, or coordinates are tracked and reversible. All versions of forms are stored and auditable, making it easy to trace which version was used, when, and by whom.
3. Geography-based planning and execution
Building on the previous two points, IASO enables precise data collection planning and execution by geography. Administrators can assign specific users or teams to zones for a given period and with dedicated forms. Campaign managers can define who collects what, where, and when.
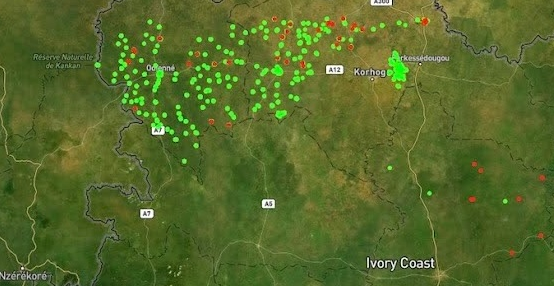
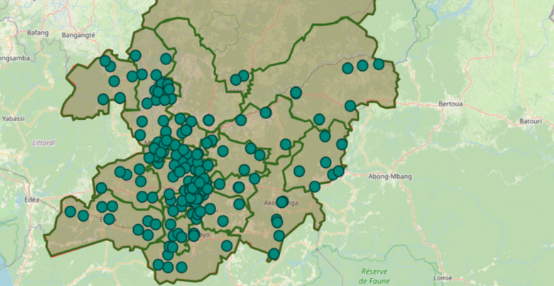
4. Powerful, map-based visualizations
Because these assignments are tied to the geographic registry, and as IASO integrates geospatial data such as Geopackages, data collected flows naturally into map-based dashboards that provide clear, real-time views of activities. This makes it easier to see coverage, identify gaps, and adjust plans thanks to heat maps.
Other tools, while strong in individual form deployment, typically require external systems or manual organization to reach this level of map-driven oversight and decentralized accountability.
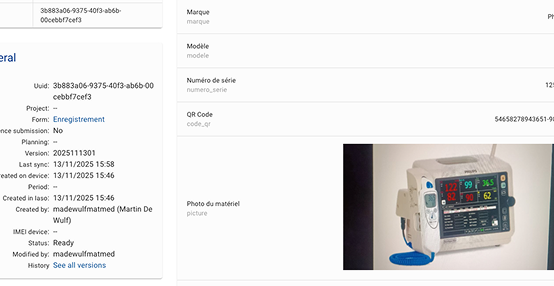
5. Entities and workflows built in
IASO also includes an entity management system to track units such as individuals or items over time. These entities can be linked to submissions and updated through multiple data collection rounds—ideal for monitoring visits, supervision, or asset tracking.
On top of this, IASO integrates a workflow engine supporting multi-step processes and validation by different actors. Because these processes are tied to geography, data administration and validation can also be decentralized, with local teams responsible only for their own areas. This ensures both scalability and accountability across large, multi-actor operations.
Organizations like the World Food Programme are already using these capabilities to coordinate nutritional programs across hundreds of sites.
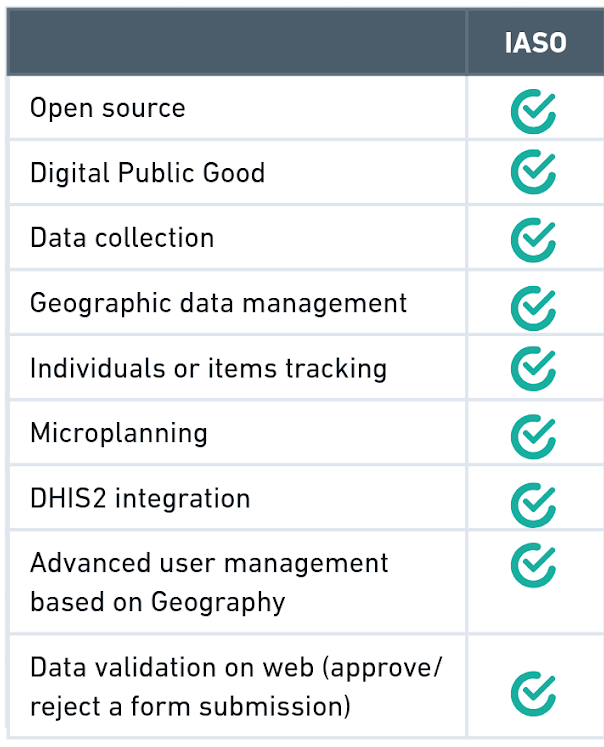
IASO’s differentiating features
Developed for health, ready for any sector
Although IASO was originally created to support large-scale health interventions, its flexibility has made it relevant in many other domains. It has also been used for education projects and nutritional programmes tracking, and its genericity makes it shelf-ready for a wide range of other sectors such as:
- Health and social programmes beneficiary tracking
- Nutrition and food security
- Climate change and adaptation
- Environmental protection
- Water and sanitation
- Forestry and raw resource management
- Energy access
- Disaster and natural risk management
- And more.
IASO offers additional assets for coordinated, geographically distributed operations. It connects data collection to planning, structures responsibilities by geography, powers visual insights through maps, and supports complex workflows.
Want to learn more about IASO? Contact us